An article about the types of product recommendations and how they impact e-commerce business.
Nowadays, a large part of online businesses uses various types of recommendation mechanisms. Properly applied, they can significantly increase the conversion rate and revenue. This happens because customers are more inclined to use the services of a company that presents an offer most tailored to their needs and preferences.
Despite such great potential, recommendations are often not used effectively. The lack of a proper strategy can significantly reduce their effectiveness.
From this post, you will learn what recommendation engines are and how they work. You will discover the types of recommendations you can use and how to ensure their maximum effectiveness. Based on this information, you will be able to prepare an effective strategy for using recommendations in your business
Benefits of using product recommendations
The goal of product recommendations is to present users with products or services that are as closely matched to their preferences and current needs as possible. This definitely:
- makes it easier for them to find the right product or service,
- positively affects their experience,
- increases the likelihood of conversion.
Therefore, recommendation mechanisms largely shape the overall user experience in contact with a website or online store. They have an invaluable impact on how customers discover and experience a brand during interactions with the site, advertising messages, and other communication channels – such as email.
The revenue growth mentioned as one of the main benefits can be achieved by applying appropriate tactics for using recommendations, which will result in:
- increased user engagement,
- increased conversion rate,
- increased average shopping cart value.
Recommendation Engines and Their Types
Recommendation engines, in a nutshell, are mechanisms that process and filter information using appropriate predictive algorithms. As a result of the analysis, we will be able to recommend the most suitable products or services to a given user in a given context. Depending on the industry, a recommendation can be treated as:
- a product (e-commerce),
- content (publishers, news portals, blogs),
- for example, profiles of specific people (dating sites).
The specifics of the business, the target group, and the context in which the user finds themselves, influence how recommendations are generated and presented on the site. There are many models of recommendations, generated based on certain logic, which will be discussed later in the article. The basic division that takes into account the way of generating recommendations and the mechanisms used distinguishes two types of recommendations:
- global,
- personalized.
Global product recommendations
This model means recommending the same products to all users or a selected segment of users. It does not take into account the individual profile of a given customer, i.e., it does not use any advanced mechanisms or algorithms for their generation. There are 2 types of such recommendations:
- generic (general) – recommendations based only on product performance. Examples include: the most popular products or the highest-rated products.
- contextual – taking into account the context in which the user is located, such as a subpage on the site. For a category page, it could be the most popular in that category. For a product page: similar or complementary products, i.e., purchased together like accessories matched to the main product.
These recommendation methods do not require the engagement of predictive algorithms. They are not personalized in any way and are based on simple calculations, e.g., the number of views or transactions of a given product. They can also be set manually, e.g., in the case of matching accessories on a product card. Therefore, no specialized recommendation software is needed for their implementation. Often, standard functionalities of the shopping platform are sufficient.
Personalized Product Recommendations
"True recommendations" are based on individual preferences and user behaviors. Specialized tools, appropriately collected and aggregated data, and algorithms that can present suitable results after processing them are needed for their generation. We can distinguish 3 main types of algorithms.
- Collaborative Filtering – which means joint filtration. It is based on the assumption that similar users will make the same or similar decisions. The algorithm collects and analyzes data on user behavior and activity, trying to match recommendations based on products or services purchased or viewed by other similar users. These are personalized recommendations tailored to a given user but based on the analysis of other users' behaviors.
- Content-based filtering, i.e., filtering based on content. This type of recommendation focuses on products that a given user was interested in. Tracking code collects information about user behavior – which subpages they visited, which products they viewed, added to the cart, or bought in the past. The algorithm prepares recommendations based on this. It is therefore based on the similarity of items that the user previously showed interest in.
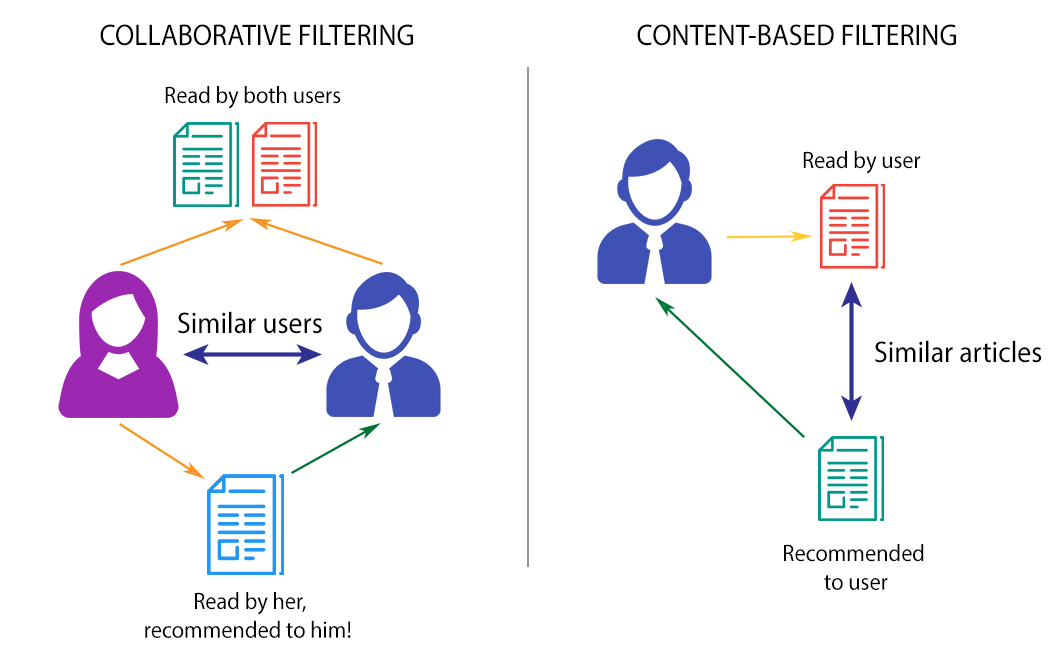
Source: https://towardsdatascience.com
- Hybrid recommendations – a recommendation technique that combines the above. It uses the "wisdom of the crowd" while also considering the individual preferences of the user. By combining both techniques, it is able to deliver the most tailored results.
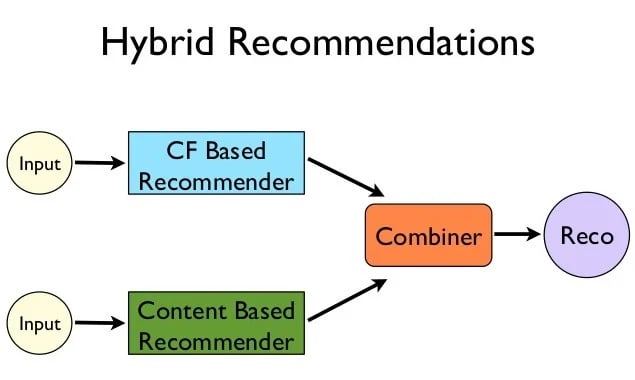
Źródło: https://www.marutitech.com
Additional recommendation setting rules
Advanced software providing recommendations allows for the inclusion of additional manually set conditions, thanks to which you can further tailor recommendations to your goals. Examples of rules you can apply to achieve specific strategies:
- use a price filter, recommending top-shelf products to users with the highest average shopping cart value;
- include specific products or subcategories to implement up and cross-selling strategies;
- use information about the user's location, taking into account weather conditions and thus recommending an adequate category of products;
- limit recommendations only to, for example, non-discounted products;
- exclude products with low stock from recommendations;
- set a priority for seasonal products.
How to Automate Marketing – strategies for using product recommendations
Proper use of recommendation potential depends on several key factors. When preparing an appropriate strategy, you should consider the following elements:
- the type of presented recommendations,
- the type of user, taking into account the data you have collected about them,
- the context in which the user is located.
Type of Recommendations
The most popular types of recommendations that you can apply in your strategy:
- Similar products;
- Purchased together;
- Most popular products/bestsellers;
- Most popular products in a given category;
- Recently viewed;
- Recently added to the cart;
- Users who viewed this product also viewed;
- Users who bought this product also bought.
AI recommendation strategies in terms of user segments
There is no one strategy that would be optimal for all users. There are those who visit your site several times a week and have a rich purchase history, others appear sporadically and have never bought anything. Another segment is new users about whom we know nothing. The most advanced recommendation tools should be able to assess the level of information they have about a given user and based on that serve them the appropriate type of recommendation. Therefore, when planning a strategy, you must determine how recommendations will be tailored to individual recipient segments and the context they are in. First, define the segments. Segregate groups of users for whom you will prepare tailored types of recommendations. Example segments might look as follows:
- new users,
- returning without purchases,
- loyal users with a cart value significantly above average,
- coming from a specific source, e.g., CPC campaigns.
Here are the strategies you can apply to them:
- New users Since we have no information about them, it would be best to display the best-selling or highest-rated products on the homepage for initial interaction.
- Returning, but without purchases In this case, we can display – for example – recently viewed products on the homepage. Having some information about such users, we can use it to display recommendations based on collaborative-filtering algorithms.
- Loyal with a high average cart value These are our most valuable users who spend the most. It's worth serving them personalized recommendations but with the application of – for example – a price filter, presenting top-shelf products.
- Users from CPC campaigns This is a specific type of users characterized by a high bounce rate. They land on a category or product page. A good way to "keep" them on the site and encourage further interaction would be to display recommendations including the best-selling products on promotion.
User context and site placement
There are many places on a store's site where you can place product recommendations. Below are discussed the basic types and techniques of recommendations and the places where they work best.
Product recommendations on the homepage
The homepage is often the first thing users see when visiting the site from direct traffic or Google search with brand queries. The homepage is somewhat a business card of our service. Such users do not necessarily look for something specific, so the role of recommendations on the homepage is to inform about the latest offer, current promotions, special offers, and the entire range of available products. Types of recommendations that work best on the homepage.
- Most popular products / bestsellers – for new users based only, while for returning ones already personalized based on collected data.
- Highest-rated products – other users' ratings can be an important element of so-called "social proof" – influencing increased engagement.
- Most popular seasonal products.
- Recently viewed products – for returning users.
- Personalized recommendations – for returning users tailored based on their previous behavior on the site and purchase history. Compared to previous types of recommendations, they can increase the sale of products from the so-called "long tail" because the algorithm will select unique products suited to the specifics of a given user, which probably would never appear on the list of bestsellers or highest-rated.
Example of recommendations from a SUP board store, where a returning user will see the last boards they viewed. This allows them to easily return to previously browsed products. This is particularly important when we talk about complex, expensive products where the decision-making process is longer. As in the case of SUP boards, which are a significant expense and the user will likely need several visits to make a final decision.
Source: Campsup.pl
Recommendations on category pages
The goal of category pages is simple – to help the user find the products they are interested in as easily as possible. Since we already know which category they are interested in, we can display:
- Most popular in that category, for new users.
- Personalized offers from that category, taking into account user preferences (for returning ones).
Recommendations on product pages
This is where visitors find detailed product descriptions. They can check all its parameters, read reviews, and add to the cart, starting the purchase process. The main goal of recommendations on these pages is to propose similar products to the currently viewed one, making it easier for them to take the "next step" in further searching for the interesting item and thus keeping them in the purchase funnel. The best tactic for this purpose will be to show them recommendations from:
- Similar products – to the currently viewed item
Another option is to present complementary products to increase the shopping cart value:
- Purchased together
- Customers who bought product X also bought – product recommendations implementing cross or up-selling strategies.
Such recommendations can be set in separate frames or combined, presented together in one block.
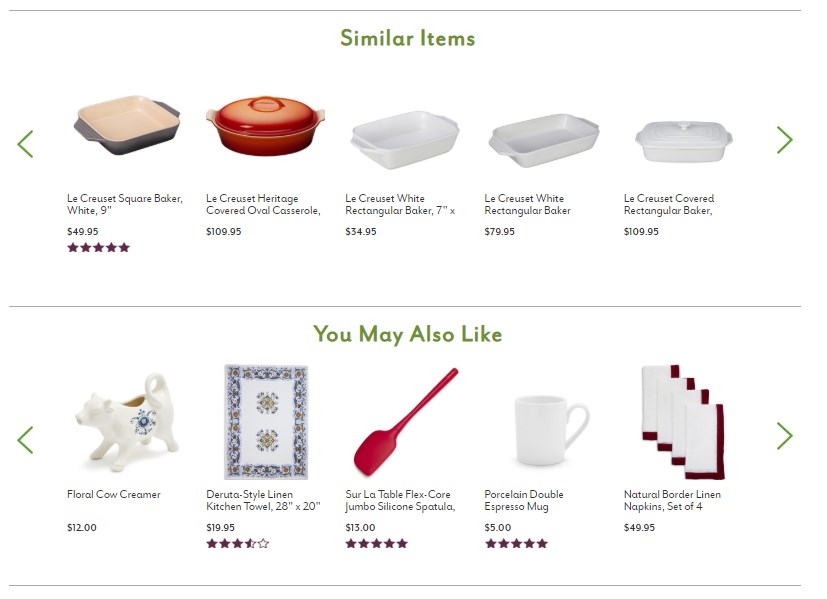
Recommendations in the shopping cart
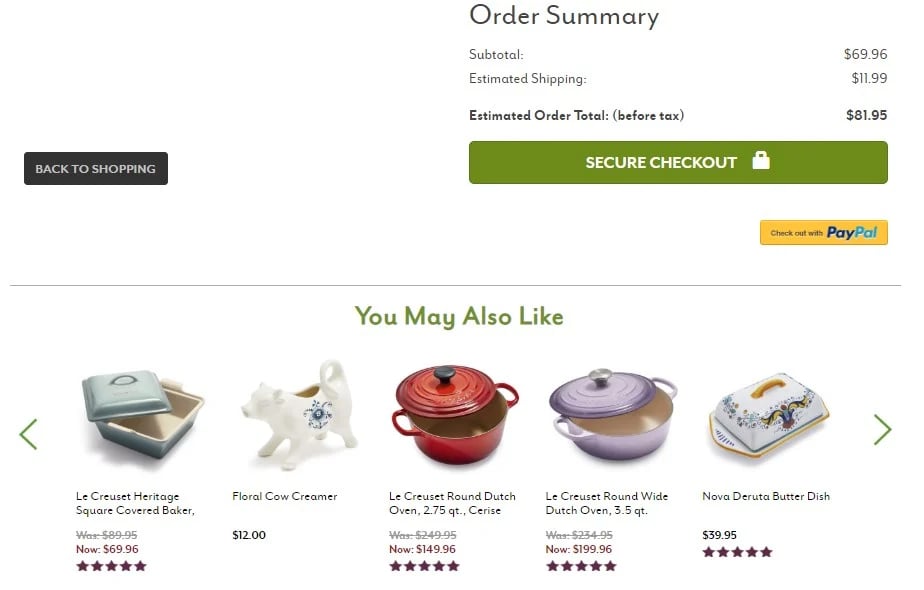
Another place where you can, and indeed should, apply recommendations is the shopping cart page. This is a very specific moment in the user's purchase path. The moment when the user has most likely already decided to make a purchase. Therefore, they will be more willing to agree to buy additional products. This makes it one of the most effective places to apply recommendations. Therefore, although there are definitely fewer views on the cart than on category or product pages, their high effectiveness means that they can have a significant impact on the results achieved. Using AI recommendations through tooltips gives you the opportunity to increase the cart value.
- Purchased together – complementary products that will increase the cart value.
- Items previously viewed – but not added to the cart.
- Similar products – if the industry's specificity is such that users buy more than one product from the same category, it is also worth adding this type of recommendation.
Summary
I know, a lot of information for one post. However, thanks to this, we have a complete guide on how to maximize the potential of product recommendations. Remember, it's not enough to throw a recommendation frame on the product card and expect amazing results. Plan a strategy, think about: what, to whom, and where you want to display, and I guarantee you, the results will be more than satisfactory.






.jpg?width=300&name=Frame%204728%20(1).jpg)
.jpg?width=300&name=Ok%C5%82adka-Rekomendacje%20produktowe%20(1).jpg)